Metabolism Calculator
Your metabolic rate is how much energy your body consumes per day, in the form of kilocalories (aka, food calories). This calculator seeks to estimate how much of your metabolism comes from when you are resting; also known as your basal metabolic rate, or resting energy expenditure.

Most of the calories you consume in a day will go towards your organs, such as your brain, kidneys, liver, and bone marrow. However, you will also spend calories on any additional activity you do, such as work or exercise.
Knowing how many calories your body consumes a day without exercise can help you figure out how many calories you should be consuming every day at minimum. If you want to lose weight, cutting calories to be slightly below your daily requirements will cause your body to source calories from adipose tissue (aka, "fat").
About this Calculator
This calculator uses basic anthropometric measurements to try and estimate
your minimum required daily caloric intake. It is very difficult to accurately estimate
your caloric requirements without using medical imaging, such as DEXA, CT, or MRI scans.
Several of the more advanced models will try to guess your fat mass and skeletal muscle mass.
If the guesses are wrong, then the resulting metabolic rate will be wrong, too.
Please only use this calculator for educational purposes, and avoid using it if you have
an adrenal or thyroid condition.
About You
Your sex and age are used in many estimations to generalize your skeletal muscle and fat mass.
Age
Sex
Body Measurements
Your weight, body fat, and height are frequently used to estimate your metabolic activity.
Using your measurements below, the calculator will predict your skeletal muscle mass and fat mass. 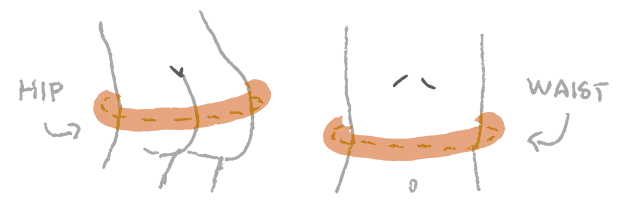 Your waist is the thinnest part of your torso above the navel. If you don't know where that is,
then measure about 3 inches or 8 cm above the belly button.
Your waist is the thinnest part of your torso above the navel. If you don't know where that is,
then measure about 3 inches or 8 cm above the belly button.
Your hip is the widest part of your hip area, within the pelvis. Keep your feet together when measuring.
Try to stand up straight and relax your body while taking waist and hip measurements.
Waist and hip measurements should be skin-tight and exactly horizontal.
Weight
Height
Waist Circumference
Hip Circumference
BMI
Unknown
PBF
Unknown
Waist-Hip-Ratio
Unknown
Models
In each box below is an individual model that is potentially capable of giving you an estimate of your
basal metabolic rate. It is very difficult to properly estimate your metabolic rate from
simple measurements like we are doing here, so please make sure all of the provided values seem reasonable.
Some models do not include energy expended from daily sedentary activity, such as walking.
Please measure and add sedentary-activity calories to the final value.

Columbia Obesity Research Center Model
This calculator does not include any calories from sedentary activities, such as household chores or walking.
This model of metabolic rate was the result of a collaboration between researchers from two institutions,
the Christian-Albrechts University and Columbia University. This model predicts your metabolic rate using your estimated skeletal muscle mass and estimated adipose tissue (fat) mass.
The accuracy of this model is not known, as it has not been assessed by independent studies, but it is probably fairly accurate for healthy adults aged 18-50.
This calculator does not include any calories from sedentary activities, such as household chores or walking.
Skeletal Muscle
Unknown
Adipose Tissue
Unknown
Metabolic Residual
Unknown
Mass-BMR
Unknown
Basal Metabolic Rate
Unknown
Nelson & Cunningham Equations
This calculator does not include any calories from sedentary activities, such as household chores or walking.
The Nelson and Cunningham equations use your modeled fat mass and lean mass to estimate your basal metabolic
rate. The Nelson equation has a known tendency to underestimate your actual resting rate, while the Cunningham
equation is known for being fairly accurate in athletes.
The method that the Nelson and Cunningham models use has shown promise in a wide variety of populations according to
independent studies. Lean-mass calculators are most likely the best choice for the majority of adults.
The Nelson model is considered accurate within 300kcal, while the Cunningham model is considered accurate within 150-250kcal (depending on who you ask).
This calculator does not include any calories from sedentary activities, such as household chores or walking.
Adipose Tissue
Unknown
Lean Tissue
Unknown
Nelson (BMR)
Unknown
Cunningham (BMR)
Unknown
Harris-Benedict & Mifflin-StJeor Equation
These are two simple linear regressions of height, weight, and age. Mifflin-StJeor is a slight refinement
over the original Harris-Benedict equation.
They both have accuracy problems, with Harris-Benedict accurate to around 450kcal,
and Mifflin-StJeor accurate to about 250kcal. They should be treated as rough estimates only.
Harris-Benedict (REE)
Unknown
Mifflin-StJeor (REE)
Unknown
Institute Of Medicine Equation
This calculator assumes basic household activity, such as chores, errands, cleaning or gardening.
This estimate is computed from an equation published by the Institute of Medicine in 2002.
This method does not aim to calculate your basal metabolic rate, but instead aims to calculate how many calories
are required to maintain your current weight.
It has been promoted by the U.S. Department of Agriculture as a reliable source for calculating your required
daily intake.
This calculator assumes basic household activity, such as chores, errands, cleaning or gardening.
Total Daily Energy Expenditure
Unknown
Bibliography
Al-Gindan, Yasmin Y et al. “Derivation and validation of simple equations to predict total muscle mass from simple anthropometric and demographic data.” The American journal of clinical nutrition vol. 100,4 (2014): 1041-51. doi:10.3945/ajcn.113.070466 Al-Gindan, Yasmin Y et al. “Derivation and validation of simple anthropometric equations to predict adipose tissue mass and total fat mass with MRI as the reference method.” The British journal of nutrition vol. 114,11 (2015): 1852-67. doi:10.1017/S0007114515003670 Balci, Aydın, et al. "Current predictive resting metabolic rate equations Are Not sufficient to determine proper resting energy expenditure in Olympic young adult national team athletes." Frontiers in physiology 12 (2021): 625370. Henry, C J K. “Basal metabolic rate studies in humans: measurement and development of new equations.” Public health nutrition vol. 8,7A (2005): 1133-52. doi:10.1079/phn2005801 Heymsfield, S B et al. “Human energy expenditure: advances in organ-tissue prediction models.” Obesity reviews : an official journal of the International Association for the Study of Obesity vol. 19,9 (2018): 1177-1188. doi:10.1111/obr.12718 Heymsfield, Steven B et al. “Simple Skeletal Muscle Mass Estimation Formulas: What We Can Learn From Them.” Frontiers in endocrinology vol. 11 31. 5 Feb. 2020, doi:10.3389/fendo.2020.00031 Macena, Mateus de Lima, et al. "Estimates of resting energy expenditure and total energy expenditure using predictive equations in adults with overweight and obesity: a systematic review with meta-analysis." Nutrition Reviews 80.11 (2022): 2113-2135. Ofenheimer, Alina, et al. "Reference values of body composition parameters and visceral adipose tissue (VAT) by DXA in adults aged 18–81 years—results from the LEAD cohort." European journal of clinical nutrition 74.8 (2020): 1181-1191. Tchernof, A., E. T. Poehlman, and J. P. Despres. "Body fat distribution, the menopause transition, and hormone replacement therapy." Diabetes and Metabolism 26.1 (2000): 12-21. ten Haaf, Twan, and Peter J M Weijs. “Resting energy expenditure prediction in recreational athletes of 18-35 years: confirmation of Cunningham equation and an improved weight-based alternative.” PloS one vol. 9,9 e108460. 2 Oct. 2014, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0108460 Wang, Z et al. “Mechanistic model of mass-specific basal metabolic rate: evaluation in healthy young adults.” International journal of body composition research vol. 9,4 (2011): 147.